Micro-perforated panels
Numerical simulation of micro-perforated panels, where the coupled system has thermal, structural and acoustical interactions
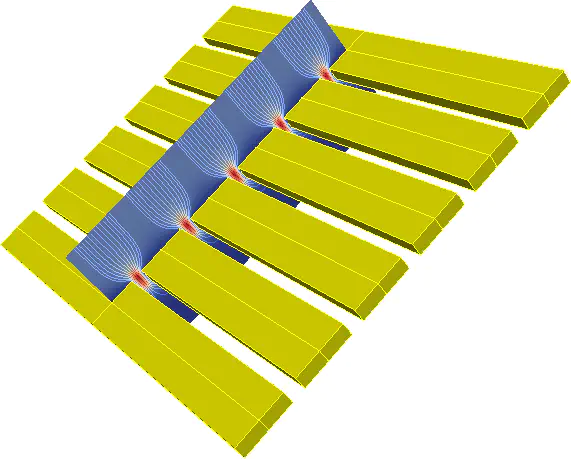 Vertical cut of the pressure field and velocity streamlines
Vertical cut of the pressure field and velocity streamlinesThe goal of this case study is focus on the numerical simulation of the dynamical behavior of a Micro-Perforated Plate (MPP), which plays the role of an structural actuator, and its effects on the pressure waves propagated along a duct. Since the objective of the actuator unit consists in minimizing the amplitude of such waves, the optimal adaptive strategy for the actuators depends on a reliable simulation of the propagation phenomena involving: an accurate simulation of the thermal and viscous boundary layer present of the compressible fluid around the MPP and the elastic structural behavior of the MPP material (see reference [1]).
Once these three models are coupled, a mixed Finite Element formulation in terms of the fluid temperature, the displacement vector field of the MPP structure and the pressure and velocity fields in the fluid is used to compute the numerical approximation of the pressure and velocity differences between in-front and back regions separated by the MPP.
Figure on the top shows a vertical cut on a section of the plane perpendicular to the MPP, where the pressure field and the velocity streamlines are plotted. In this numerical simulation, the MPP (depicted in dark yellow) has been designed with micro-slits. As in this proposed collaboration project, the simulation code has been developed specifically to handle accurately the thermal-structural-acoustic interaction of the MPP with the duct fluid.
References
[1] A. Bermúdez, J.L. Ferrín, A. Prieto.Numerical characterization of the acoustic impedance for micro-perforated plates (MPP).
Book of Abstracts at Euronoise 2012. Prague, 10-13 June (2012)